A framework for managing and maintaining multi-language pre-commit hooks.
A few weeks ago I came across pre-commit.
It’s a pretty useful framework, to generate pre-commit hooks that are used to check code, before
committing it to your branch. It’s pretty popular in the python community, but also provides
it’s functionality for multiple languages. For more see the list of
supported languages.
Hooks
Without any hooks pre-commit doesn’t make a lot of sense, so let’s see what these hooks do. Hooks are small programms that check your committed changes and raise an error (status code 1) if your commits do not pass the hooks check. Basically pre-commit holds the foot into the door, if you’r committed changes not following the spec put up by your hooks config. So it prevents you from committing code with low quality. The diagram below illustrates this behaviour:
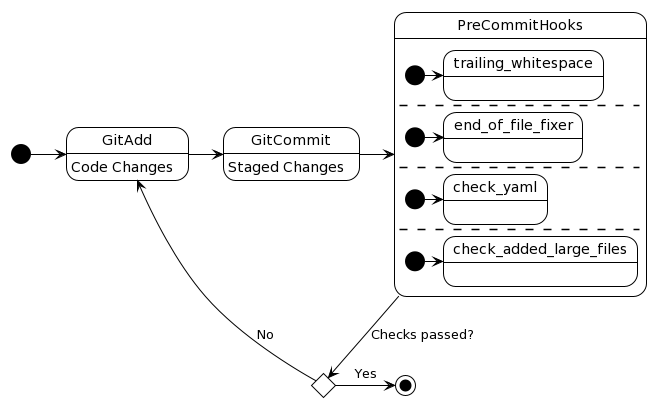
Get started
- Install with
brew install pre-commitorpip install pre-commit - Go to the top of your repo
- Create a config file with
touch .pre-commit-config.yaml - Fill your config with a sample file
pre-commit sample-config > .pre-commit-config.yaml - Install pre-commit-hooks in your repo
pre-commit install
With pre-commit sample-config > .pre-commit-config.yaml we filled our config file with pre-commits
default content. The .pre-commit-config.yaml now contains the following
# See https://pre-commit.com for more information
# See https://pre-commit.com/hooks.html for more hooks
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v3.2.0
hooks:
- id: trailing-whitespace
- id: end-of-file-fixer
- id: check-yaml
- id: check-added-large-files
It says take hooks from repo with id: trailing-whitespace. So pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
provides multiple useful hooks, you can simply plug in. See the list of officially supported hooks
here.
Other hooks
One example for other hooks/executable programms could be black (a python formatter). The repo your
adding has to have a .pre-commit-hooks.yaml file. This file tells pre-commit where the executable (entry)
is, what language is uses (language) or for example what files it’s running on files
(the latter is a pattern). Most important it tells what id to use in the config file.
You can add it and it’ll be executed on commit (or the stage you want to to be execeuted, more about this later).
Add black like this:
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/psf/black
rev: 22.6.0
hooks:
- id: black
Please have in mind the rev value does not automatically updates if you run
pre-commit autoupdate For more about this see
blacks-documentation.
Further external hooks will also define a .pre-commit-config.yaml file. It’ll tell your config file which
defaults to use for configuration.
Configure hooks
The above example, just tells pre-commit to take a set of hook ids from a repo. In case of black, you’d configure
the formatter using [[tool.black]] in a pyproject.toml, but there’s a more to configure, on the pre-commit side.
As mentioned in other hooks, defaults are coming from the source repos .pre-commit-config.yaml file.
You can overwrite these in your .pre-commit-config.yaml. See the list of possible arguments at pre-commits
documentation.
A good example is stages or always_run. always_run is pretty self-explainatory. stages can configure
when the hook is running. Possible values: commit, merge-commit, push, prepare-commit-msg, commit-msg, post-checkout,
post-commit, post-merge, post-rewrite, or manual. If you install the hooks with -t or --hook-type you also can
tell the hook when it should run. Default is all-stages. To install all your hooks to run on push would be
pre-commit install --hook-type push.
If you want to see how a hook works, you can execute a single hook with pre-commit run <hook-id>. In case you
develop your own hook pre-commit try-repo is a nice solution to test
a hooks behaviour. For your own custom hook development have a look at:
Develop your own hook
In order to learn how pre-commit hooks are build, I’ve developed a hook that checks if the current requirements.txt file of a
python project is in sync with pyproject.toml and the currently used poetry environment (poetry run which python).
This hook is called poetry-requirements and is helpful if your repository
needs a requirements.txt for things like heroku deployment or building a docker container in a github action
(you don’t have to install poetry in the action to do that). Basically if you need a requirements.txt and you want to work with
poetry for things like environment and dependency management, this hook can do the trick.
Basically it’s a python cli wrapper for poetry export. An ArgumentParser takes care of the arguments and the main.py runs a
diff between requirements.txt and the output of poetry export.
Here’s a small guiding list to build your own hook:
- Define the arguments you need on cli
- Build the CLI tool
- Define defaults for your tool in
.pre-commit-hooks.yaml - Create a sample
.pre-commit-config.yamlfor others to use your tool.
To test your repo you either test it in the repo of your hook or setup a test repo. In any case you can execute the following command in your testing repo:
pre-commit try-repo <path/repo/to/repo> <hook-id>
In order to get started see poetry_requirements/main.py. But beaware that main.py#L72 is a commented, which you likly need if you’r hook runs on a set of files.
The best examples are coming from pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks.
An opinionated list of awesome hooks
This is my go to default pre-commit hooks
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v4.3.0
hooks:
- id: trailing-whitespace
- id: end-of-file-fixer
- id: check-yaml
- id: check-added-large-files
- id: debug-statements
- id: detect-private-key
- id: pretty-format-json
- id: check-added-large-files
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pygrep-hooks
rev: v1.9.0
hooks:
- id: python-use-type-annotations
- repo: https://github.com/asottile/reorder_python_imports
rev: v3.8.2
hooks:
- id: reorder-python-imports
args: ['--application-directories=.:environment_sound_classification', --py37-plus]
- repo: https://github.com/psf/black
rev: 22.6.0
hooks:
- id: black
- repo: https://github.com/pycqa/flake8
rev: 5.0.4
hooks:
- id: flake8